With the onset of cold weather, hydrangeas begin to require special care. In order for the plant to bloom profusely and look healthy next summer, it must be properly prepared for wintering.

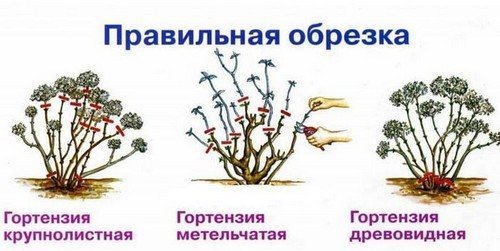
The most important thing is proper pruning, which is usually done in spring or autumn. Regardless of the time of year in which pruning is done, it is always important to remove faded, dried inflorescences. You can prune the bush immediately after it blooms, but this can be done even in winter. There are three types of this plant, each of them has its own pruning methods.

Tree hydrangea pruning
For this type of hydrangea There are four types of pruning:
- Rejuvenating - produced with the aim of removing weak, thin shoots.
- Sanitary – carried out with the aim of removing all dried, broken branches. With this type of pruning, all branches except the top ones are removed.
- Pruning to enhance flowering - done after the plant has flowered, all main branches are shortened to 2-4 well-developed buds.
- Thinning - needed if the plant is too thick and many branches grow inward; with this type of pruning, all zero shoots are removed.

Pruning paniculate hydrangea
For this type of hydrangea, autumn pruning is extremely necessary, since if it is not carried out, the bush will turn into an untidy ball in a few years, clogged with shoots and, due to the abundance of inflorescences, it simply will not have the strength to bloom, and the new inflorescences will be weak and faded.The main thing in autumn pruning of this species is to thin out existing shoots by removing all non-viable branches.
Pruning large-leaved hydrangea
You need to be especially careful when pruning this species so as not to deprive it of its ability to bloom. The most important thing is to preserve the shoots formed in the spring that have not yet bloomed. The rest - old, diseased and faded branches - can be safely removed.
Transplanting hydrangeas in the fall
Only tree-like and paniculate species are suitable for autumn replanting, but the place for their replanting must be prepared in advance, in the spring. The choice of landing site should be taken seriously. Hydrangea loves sunny places; it is worth transplanting it to a place where it will not be shaded by other bushes. The planting hole should be deep, about fifty centimeters and quite spacious. In order for the bush to take root in a new place, fertilizers, humus, peat, and sand are added to the hole. It is important to remember that when replanting in autumn in the spring, you will need to remove all the inflorescences, then the bush will grow and bloom better. Perhaps after transplantation the inflorescences will change color, this is due to changes in soil acidity.
Propagation of hydrangeas in autumn
There are several methods of reproduction.
- cuttings are the most common propagation method among summer residents. The branches remaining after pruning the bush are carefully cut into cuttings for further cultivation;
- using seeds is not a very effective method, since you are never sure whether the seeds will sprout and whether the shrubs obtained from them will then take root;
- root cuttings - a simple but rarely used method, with which you can get many young bushes already in the spring, when the plant wakes up and shoots begin to appear.
The main rule for any method of propagation is to monitor watering. The plant loves moisture very much, without it, the middle-aged shoots will die very quickly.

Rule for watering hydrangea in the fall
With the onset of cold weather, watering should be made more moderate or stopped altogether, since it often rains in the fall and the bush no longer needs frequent watering. With excess moisture, cracks and chips begin to form on the stems and branches of the bush. To protect the plant from natural moisture, you can dig a shallow ditch around the bush to drain excess water, or cover the bush with film. Growing a "forest for a panda" - bamboo thickets will decorate any area
During its flowering period, hydrangea loses a lot of strength, which can be restored by fertilizing with fertilizers before the dormant period, which occurs in winter. Fertilizers are used to strengthen the root system of the plant, they help the plant bloom abundantly and develop. You should not postpone fertilizing, early varieties should be fertilized by the end of August, and later ones in early September. It is important to remember that at least a month should pass from the last fertilizing to the first frost. Various fertilizers are used for fertilizing:
organic fertilizers (manure, peat, compost),
- potassium-phosphorus (strengthen the root system),
- mineral fertilizers (maintain the acidity level of the soil).
- You need to be careful with the latter, do not put too much, an excess of mineral fertilizers will cause more harm to the bush than good.root cuttings - a simple but rarely used method with which you can get a lot of young bushes in the spring, when the plant wakes up and shoots begin to appear.
The main rule for any method of propagation is to monitor watering. The plant loves moisture very much; without it, middle-aged seedlings will die very quickly.

With the onset of cold weather, watering should be made more moderate or stopped altogether, since in the fall it often rains and the shrub no longer needs frequent watering. When there is excess moisture, cracks and chips begin to form on the stems and branches of the bush. To protect the plant from natural moisture, you can dig a shallow ditch around the bush to drain excess water, or cover the bush with film.













How to prune grapes correctly in autumn