Among cucumber diseases, ascochyta blight is considered one of the most dangerous. The disease is more common in greenhouses, but can also affect plants in open ground. The pathogenic fungus does not manifest itself at first. Symptoms of ascochyta blight appear at a late stage, making treatment difficult. The disease manifests itself most clearly towards the end of the growing season. However, it is possible to cope with it.
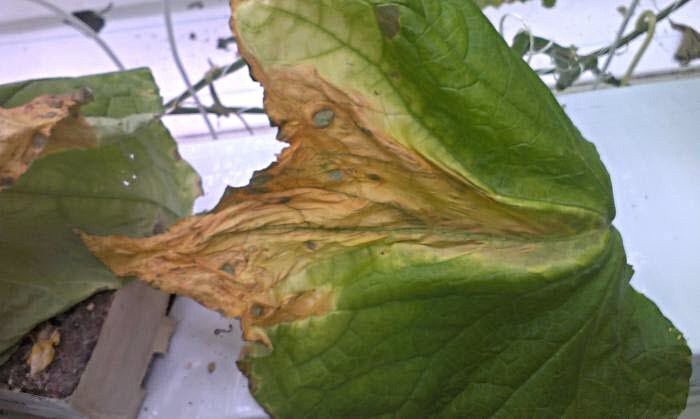

Manifestations of ascochyta blight on cucumbers
Regular inspection of cucumbers will help identify symptoms of ascochyta blight. The disease manifests itself:
- the appearance of gray watery spots on the lashes, which later lighten;
- the appearance of pockets of black rot on thin sections of stems;
- change in leaf color (turn brown);
- Ulcers or mucus appear on the fruits, and later the cucumbers rot.
The development of infection is facilitated by high humidity, excess nitrogen fertilizers, and warm weather. Fungal spores are carried throughout the area by wind or pests. The natural reservoir for the pathogen is weeds. Ascochyta blight often develops when cucumbers are planted in dense areas.
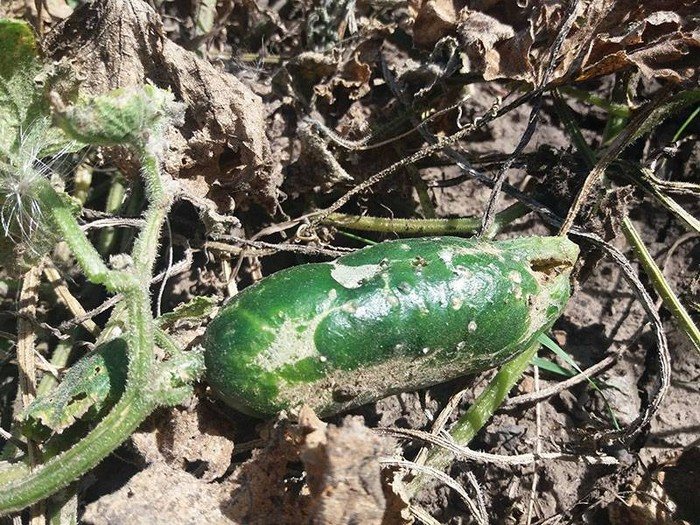

Treatment options
The disease can be treated with chemical and biological drugs. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Chemical-based products act quickly and effectively, but are harmful to the environment. In addition, in this case it is necessary to observe a waiting period before harvesting the fruits.
Biological fungicides are harmless, but their effect is weaker. You will have to wait for some time for the effect. In the future, repeated treatments of the plantings will be required. Folk remedies do not work against this disease, so it is better not to waste time waiting for the effect of their use.
Chemical fungicides
Preparations based on copper and some chemical compounds cope well with the causative agents of ascochytosis. In this list:
- Bordeaux mixture. The solution is prepared in a 1% concentration. The bushes are treated on the leaves once every 10-12 days.
- A mixture of chalk and copper sulfate. The components are used in equal quantities. The resulting powder is sprinkled on the ulcers on the stems at the onset of the disease.
- "Topaz". Systemic drug. The active ingredient is penconazole. Available in 2 ml ampoules. Before use, dilute one package of the preparation in 10 liters of water. Repeat the treatment after 2 weeks.
- "Fundazol". A fungicide based on benomyl. Copes with many fungal diseases, has a systemic effect. Available in the form of a powder soluble in water. Provides protection for up to 10 days. To prepare the solution, use 10 g of the preparation per bucket of water, after which the plants are sprayed.
If last season the cucumbers in the greenhouse suffered from ascochytosis, it is necessary to treat the soil and the walls of the building with a 5% concentration of formalin solution. For each square meter of the garden bed, use 1 liter of the prepared composition.

Biological preparations
The main components of biological preparations are beneficial mushrooms and soil bacteria, as well as their metabolic products. For the treatment of ascochytasis the following is used:
- "Trichotsin SP". Biological fungicide is available in powder form. The drug is dissolved in a small amount of heated water and then diluted to the required volume. Dosage – 6 g per 10 liters of water. Water the soil with a fungicide solution and spray the cucumbers.
- "Trichodermin." Suitable for treating seeds before sowing. In the future, it is used when signs of the disease first appear. To prepare the solution, use 80 g of liquid concentrate per 10 liters of water. The drug is sprayed on the ground and plantings.
Treatments are repeated every 10-15 days until the effect occurs. Spraying is carried out in cloudy weather or in the morning before the active sun arrives.
Preventive measures
To prevent cucumbers from getting ascochyta blight, it is better to take care of prevention. Preventive measures include:
- soaking seeds before sowing in a fungicide solution;
- soil disinfection before planting;
- regular thorough inspection of cucumbers;
- mulching the beds;
- compliance with watering standards;
- ventilation if cucumbers grow in a greenhouse.
Prevention includes choosing varieties that are resistant to ascochyta blight. In this case, there is a corresponding mark on the packaging.

Fungal diseases are insidious because they have a long incubation period and at first do not manifest themselves in any way. That is why it is better to take preventive measures in advance. If signs of the disease do appear, biological and chemical drugs are used until the result is obtained.